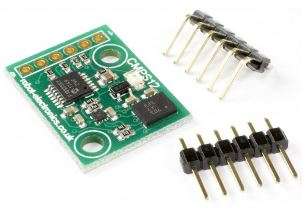
The CMPS12 is our 4th generation tilt compensated compass. Employing a 3-axis magnetometer, a 3- axis gyro and a 3-axis accelerometer. At the core of the module is the superb BNO055 running algorithms to remove the errors caused by tilting of the PCB. Power supply requirements are flexible, you can feed between 3.3 – 5v and the module draws a nominal 18mA of current. A choice of serial or I2C interfaces can be used for communication.
Overview of outputs Heading, 16 bit – 2 outputs, one calculated by Bosch and one by us Heading, 8 bit – 0-255 scaled for simpler requirements Pitch – +/- 0-90° or +/- 0-180° Roll – +/- 0-90° Temperature – current temperature of the BNO055 in °c Raw sensor outputs – 3 x 16 bit integers for each of the Magnetometer, accelerometer and gyro Mode selection Serial or I2C mode is easily selected with the state of the mode pin. Note the CMPS12 looks at the mode selection pin at power-up only.
For I2C the mode pin can be left open or pulled to the supply voltage, for serial mode the mode pin should be connected to 0v ground.
Power – 3.3v-5v 18mA Typ.
Resolution – 0.1 Degree
Accuracy – Better than 1%. after calibration
Signal levels – 3.3v, 5v tolerant
I2C mode – up to 400khz
Serial mode – 9600, 19200, 38400 baud
Full Technical Data
We also have a free design for a 3d printed tower here
Examples:
I2C bus tutor – general I2C guide
Arduino – I2C interface or a serial interface and displaying data via the serial monitor
ATMEGA32 – reading the result and displaying on a LCD03/LCD05
PIC18F4410 – reading the result and displaying on a LCD03/LCD05
PIC24FJ16GA002 – reading the result and displaying on a LCD03/LCD05
Picaxe18x – I2C communication example
Raspberry Pi – using I2C communication