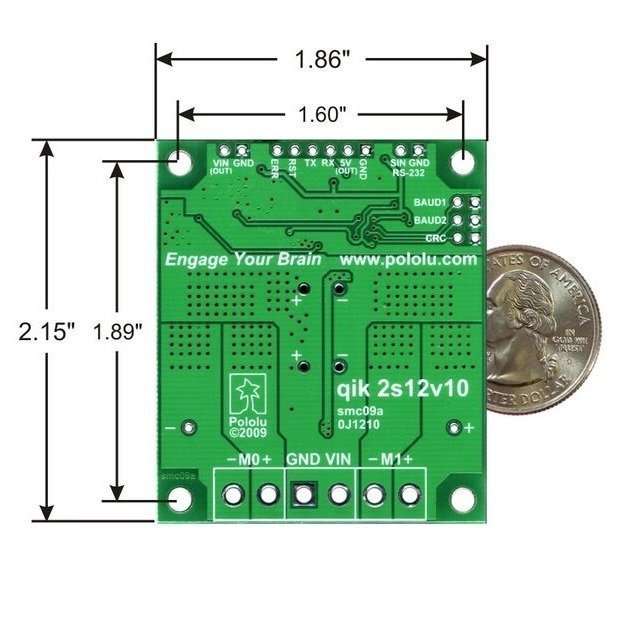
Dimensions [1]
| Size: | 1.86″ x 2.15″ x 0.28″ |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 14 g |
General specifications
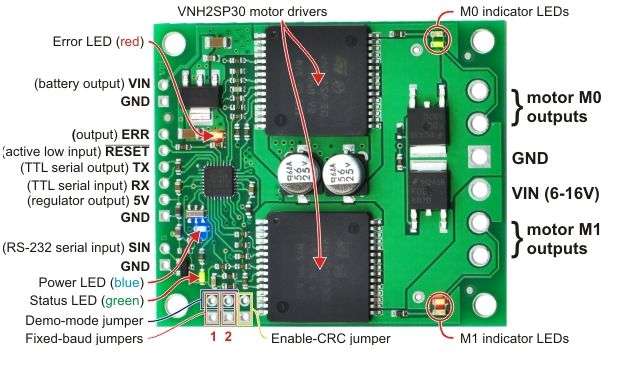
| Motor driver: | VNH2SP30 x2 |
|---|---|
| Motor channels: | 2 |
| Control interface: | non-inverted TTL serial (2-way); RS-232 serial (1-way) [2] |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 6 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 16 V |
| Continuous output current per channel: | 13 A |
| Peak output current per channel: | 30 A |
| Current sense: | 0.13 V/A |
| Maximum PWM frequency: | 19.7 kHz [3] |
| Minimum logic voltage: | 2.7 V |
| Maximum logic voltage: | 5.5 V |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | Y |
Notes
1 – Without included hardware.
2 – Autodetects baud rates between 1200 and 115,200 bps, or can be set for a fixed baud at 115.2, 38.4, or 9.6 kbps baud rate.
3 – Can also be configured to use 9.8 kHz, 2.5 kHz, 1.2 kHz, 310 Hz, or 150 Hz PWM frequencies.
Overview
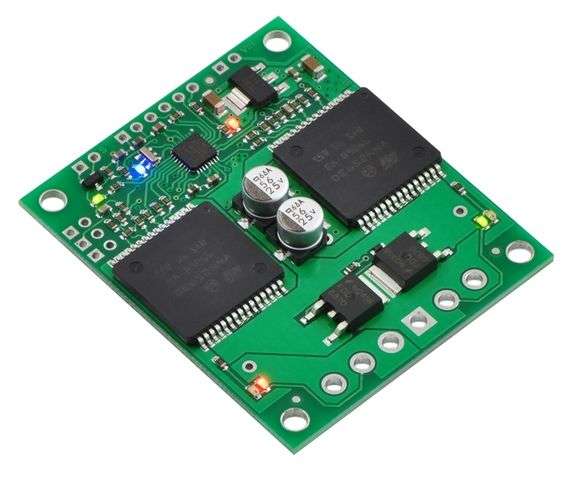
The qik 2s12v10 adds a comprehensive yet easy-to-use, high-power option to Pololu’s line of motor controllers. The compact board—it’s almost the same size as the dual VNH2SP30 carrier board by itself—allows any microcontroller or computer with a serial port to drive two brushed DC motors with full direction and speed control, providing up to 13 A (continuous) per motor channel without a heat sink and tolerating peaks as high as 30 A.
The improvements over competing products include:
- high-frequency PWM to eliminate switching-induced motor shaft hum or whine
- a robust, high-speed communication protocol with user-configurable error condition response
- visible LEDs and a demo mode to help troubleshoot problematic installations
- reverse power protection
Features
- Simple bidirectional control of two DC brush motors.
- 6 V to 16 V operating supply range.
- 13 A maximum continuous current per motor (30 A peak).
- Logic-level, non-inverted, two-way serial control for easy connection to microcontrollers or robot controllers.
- RS-232-level, one-way serial control for easy connection to a PC serial port.
- Optional automatic baud rate detection from 1200 bps to 115.2 kbps.
- Seven on-board indicator LEDs (power, status/heartbeat, error indicator, and motor indicators) for debugging and feedback.
- Advanced features include configurable acceleration, motor current feedback, and current limiting.
- Error output to make it easier for the main controller to recover from an error condition.
- Optional motor shutdown on error or serial timeout for additional safety.
- Jumper-enabled demo mode allowing initial testing without any programming.
- Optional CRC error detection eliminates serial errors caused by noise or software faults.
Specifications
| Motor channels: | 2 |
|---|---|
| Operating voltage: | 6 – 16 V |
| Continuous output current per channel: | 13 A |
| Peak output current per channel: | 30 A |
| Auto-detect baud rate range: | 1200 – 115,200 bps |
| Available fixed baud rates: | 115,200 bps, 38,400 bps, 9600 bps |
| Available PWM frequencies: | 19.7 kHz, 9.8 kHz, 2.5 kHz, 1.2 kHz, 310 Hz, 150 Hz |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | Y |
| Motor driver: | VNH2SP30 x2 |
Included Hardware
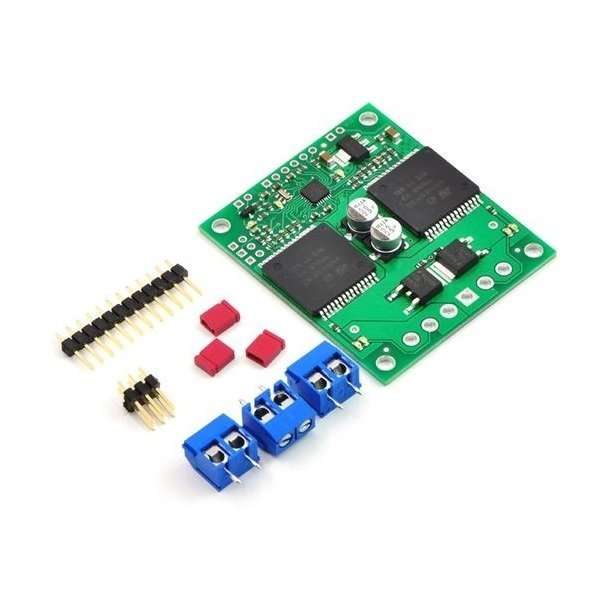
The qik ships with a 12×1 straight 0.100″ male header strip, a 3×2 straight 0.100″ male header strip, three 2-pin terminal blocks, and three red shorting blocks.
For the most compact installation, you can solder wires directly to the qik pins themselves and skip using the included hardware. For high-current installations, you should avoid using the supplied terminal blocks, which are rated for up to 15 A, and instead directly solder the motor and power supply wires to the pads.
The included hardware allows you to make less permanent connections. You can break the 12×1 header strip into a 6×1 piece and two 2×1 pieces and solder these strips into the qik’s logic pins where you plan on making connections, or you can use a pair of pliers to pull out the two header pins in the original 12×1 strip for which the qik has no holes and solder the entire strip to the qik’s logic pins. You can see this latter approach in the picture above. You can then make your own cables that have female headers on them and plug these onto the male headers on your qik, or you can solder the pins to the other side of the board and simply plug your qik into a breadboard. You might also consider using a 0.100″ right-angle male header strip (not included) for a lower profile.
The 3×2 header strip can be soldered to the jumper pins as shown above, which lets you make use of the included shorting blocks, and the included terminal blocks lock together to make a single, 6-pin strip that you can solder to the power side of the board.
Documentation and other information
User’s guide for the Pololu Qik 2s12v10 Dual Serial Motor Controller
Pololu Serial Transmitter utility for Windows
A simple serial transmitter utility for Windows that lets you transmit sequences of bytes at a selectable baud rate to a selectable COM port. This program can be conveniently used to send commands to our serially controllable devices.