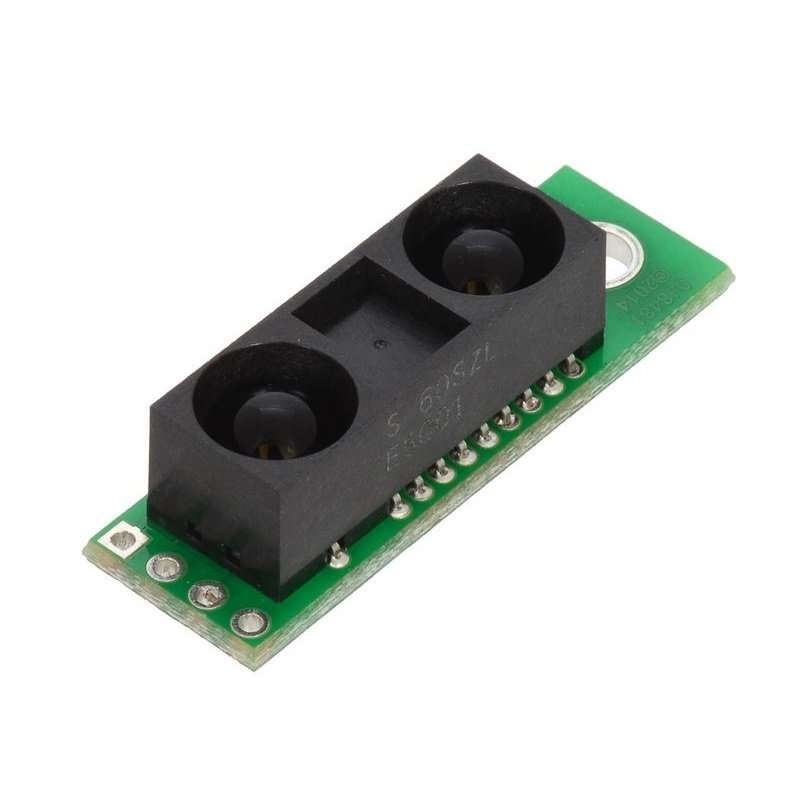
Note: The GP2Y0A60SZ distance sensor from Sharp offers a wide detection range of 4″ to 60″ (10 cm to 150 cm) and a high update rate of 60 Hz. The distance is indicated by an analog voltage, so only a single analog input is required to interface with the module. The sensor ships installed on our compact carrier board, which makes it easy to integrate this great sensor into your project, and is configured for 5V mode.
Interfacing to most microcontrollers is straightforward: the single analog output, OUT, can be connected to an analog-to-digital converter for taking distance measurements, or the output can be connected to a comparator for threshold detection. The sensor automatically updates the output approximately every 16 ms. The enable pin, EN, can be driven low to disable the IR emitter and put the sensor into a low-current stand-by mode. This pin is pulled high on the carrier board through a 10 kΩ pull-up resistor to enable the sensor by default.
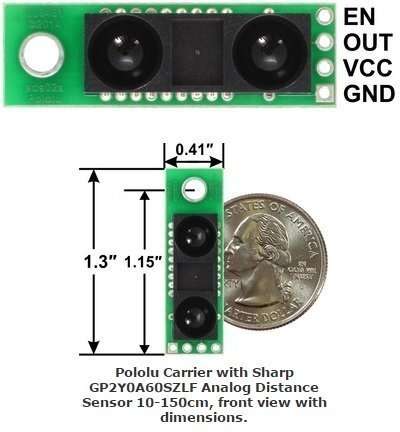
A 1×4 strip of 0.1″ header pins and a 1×4 strip of 0.1″ right-angle header pins are included, as shown in the picture below. You can solder the header strip of your choice to the board for use with custom cables or solderless breadboards, or you can solder wires directly to the board itself for more compact installations. The board features one 0.125″ mounting hole that works with #4 or M3 screws (not included); if you do not need the mounting hole, you can cut that part of the board off to reduce its size.
In 5V mode, the recommended operating voltage is 2.7 V to 5.5 V, and the output voltage differential over the full distance range is approximately 3 V, varying from around 3.6 V at 10 cm to 0.6 V at 150 cm. The GP2Y0A60SZ datasheet contains a plot of analog output voltage as a function of the distance for the two modes.
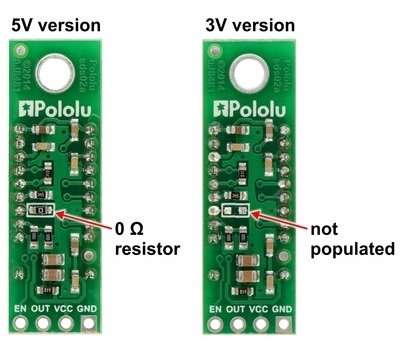
The only difference between the two versions is the presence or absence of a zero ohm resistor as shown in the picture above (the component location is marked by a rectangle on the silkscreen). You can convert a 5V version to 3V by removing the resistor, and you can convert a 3V version to 5V by shorting across the two pads.
Note that the 5V version can be powered all the way down to 2.7 V, and the relationship between the sensor output voltage and distance is mostly independent of the supply voltage. The main drawback to powering the 5V version at a lower voltage is the output voltage will not exceed the supply voltage, so the effective minimum detection distance might increase (i.e. for distances that would result in output voltages above your supply voltage, the output will instead be capped at the supply voltage). On the other hand, if you mostly care about measuring distances closer to the maximum end of the range, you could benefit from the increased output voltage differential of the 5V version even if you are only powering it at 3.3 V.
Feature summary
- Operating voltage:
- 5V version: 2.7 V to 5.5 V
- 3V version: 2.7 V to 3.6 V
- Average current consumption: 33 mA (typical)
- Distance measuring range: 10 cm to 150 cm (4″ to 60″)
- Output type: analog voltage
- Output voltage differential over distance range:
- 5V version: 3.0 V (typical)
- 3V version: 1.6 V (typical)
- Update period: 16.5 ± 4 ms
- Enable pin can optionally be used to disable the emitter and save power
- Size without header pins: 33 mm × 10.4 mm × 10.2 mm (1.3″ × 0.41″ × 0.4″)
- Weight without header pins: 2.5 g (0.09 oz)
Schematics
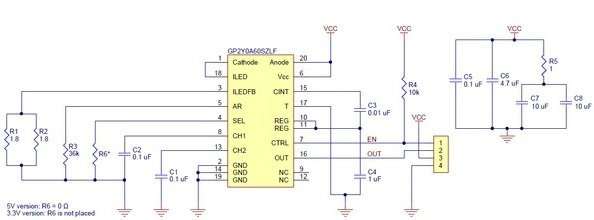
File downloads
- GP2Y0A60SZLF/GP2Y0A60SZ0F datasheet
- Pololu Carrier for Sharp GP2Y0A60SZLF Analog Distance Sensor schematic: Printable schematic for the Pololu Carrier for Sharp GP2Y0A60SZLF Analog Distance Sensor.
- Pololu Carrier with Sharp GP2Y0A60SZLF Analog Distance Sensor 10-150cm dimension diagram: Detailed dimension diagram of the Pololu Carrier with Sharp GP2Y0A60SZLF Analog Distance Sensor 10-150cm.
- 3D model of Pololu Carrier with Sharp GP2Y0A60SZLF Analog Distance Sensor 10-150cm