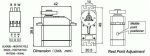
Dimensions
| Size: | 39.5 x 20.5 x 42 mm |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 60 g |
General specifications
| Speed @ 6V: | 0.14 sec/60°1 |
|---|---|
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 15.4 kg.cm |
| Speed @ 4.8V: | 0.16 sec/60°2 |
| Stall torque @ 4.8V: | 14.8 kg.cm |
| Lead length: | 11 in |
| Gear | Metal |
Notes:
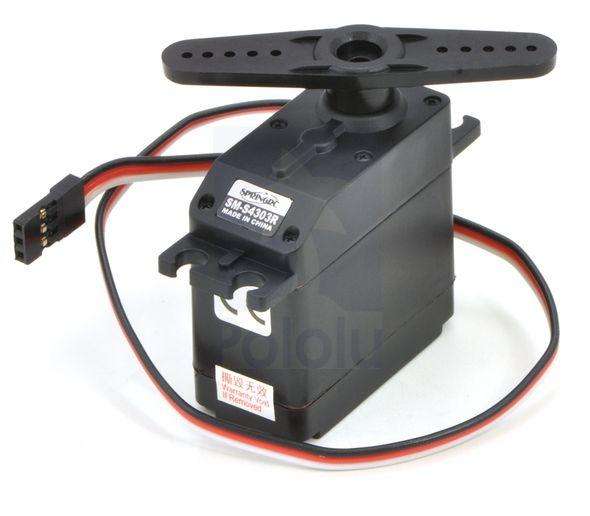
The SM-S4315R is a 15 kg.cm standard-sized servo that has been built by SpringRC specifically for continuous rotation, making it an easy way to get your robot moving. It features two ball bearings on the output shaft for reduced friction, and it offers easy access to the rest-point adjustment potentiometer. This is the strongest continuous rotation servo we carry:15.4 kg-cm and 70 RPM (no-load) at 6V.
The servo has an 11″ (270 mm) lead that is terminated with a JR-style connector and comes with the following included hardware:
The SM-S4315R is a standard-sized servo that has been built by SpringRC specifically for continuous rotation (up to 70 RPM at 6 V), and it is the strongest continuous rotation servo we carry (15.4 kg-cm at 6 V). It features an all metal gear with two ball bearings on the output shaft for reduced friction, and it offers easy access to the rest-point adjustment potentiometer. The servo can be controlled using a direct connection to a single microcontroller I/O line without any additional electronics, which makes it a great actuator for beginner robotics projects.
The SM-S4315R continuous rotation servo converts standard RC servo position pulses into continuous rotation speed. The default rest point is 1.5 ms, but this can be adjusted by using a small slotted screwdriver to turn the middle-point positioner. Pulse widths above the rest point result in counterclockwise rotation, with speed increasing as the pulse width increases; pulse widths below the rest point result in clockwise rotation, with speed increasing as the pulse width decreases. Note that this is the reverse of what is described in the datasheet.
This robotics servo is compatible with our servo controllers and has a Futaba-compatible output shaft. For detailed specifications -> Here