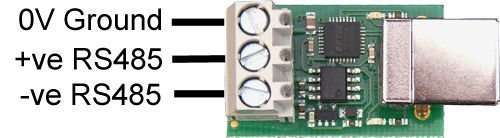
The USB-RS485 is a complete, self powered, USB to RS485 interface working at any baud rate up to 250k baud. It features automatic bus turn-around – any time your not transmitting the module is listening. Uses the MAX487 quarter power tranceiver, so you can have up to 128 devices on the bus.
USB interface uses the FTDI chip which has drivers available for Windows XP64, XP, 2000, ME, 98, CE.NET V4.2, Linux, Mac OS8, OS9, OSX.
The USB-RS485 module provides an easy to use RS485 interface by means of a Virtual Com Port on the users system. There are no command structures, whatever is sent to the Virtual Comm Port is automatically converted to RS485 and vice versa. The module is completely self powered from the USB bus.
First Step – Get The Drivers
The USB-RS485 module uses the FTDI FT232R USB chip to handle all the USB protocols. The documentation provided by FTDI is very complete, and is not duplicated here. Before using the USB-RS485, you will need to install FTDI’s Virtual COM Port ( VCP ) Drivers. These drivers appear to the system as an extra Com Port ( in addition to any existing hardware Com Ports ). Application software accesses the USB device in the same way as it would access a standard Windows Com Port using the Windows VCOMM API calls or by using a Com Port Library. Drivers are available for Windows, Apple, Linux and Open BSD systems directly from the FTDI website. You should get and install the drivers now, before you connect the USB-RS485 to your computer. The Drivers page is here.
Which COM port?
After installing the drivers, and plugging in the USB-RS485 module to a spare USB port, you will want to know which COM port it has been assigned to. This will vary from system to system depending on how many COM ports you currently have installed. To find out where it is, right click on your “My Computer” desktop icon and select the “Device Manager” tab. For XP or Vista, go to Control Panel -> System -> Device Manager. Now scroll down and open the “Ports (COM & LPT)” tab. You should see the USB serial port listed – COM2 in the example below. If you want to change the COM port number – just right click on it, select properties, select advanced and select the COM port number from the available list. The USB-RS485 supports data rates of up to 250kbps (bits).
Automatic Bus Turnaround
The RS485 bus features automatic direction turnaround. Under idle conditions, where no data is being transmitted or received, the bus will be in the high impedance listening mode. Any data that arrives on the RS485 bus will be transmitted via the USB port to the PC. When the PC transmits data the bus direction immediately turns around to transmit the data out on the RS485 bus. When the PC stops transmitting data, there is a 3uS delay to ensure that the final data high gets a firm drive before setting the bus to idle (listening mode) again.
MAX487 RS485 driver chip
The MAX487 used on the USB-RS485 module features reduced slew-rate drivers that minimize EMI and reduce reflections caused by improperly terminated cables, thus allowing error-free data transmission up to 250kbps.
Writing the PC Application
Although this is your domain, it’s always helpful to have a little starting point, so we’ve put together a couple of short articles on using the PC Serial Com. Port with Visual Basic and C#. Theses are for the Visual Express 2008 versions of VB and C#, which are currently free downloads from the Microsoft website.
Examples:
DMX generator – Program allows the USB-RS485 to be used to generate a DMX512 stream, fully controllable from Windows GUI. We also have a user manual